Introduction:
Multiple myeloma (MM) plasma cells express CD38, which is the target of isatuximab (ISA), a monoclonal antibody (mAb), approved for treatment. This systematic review aims to explore the efficacy and safety of ISA based regimens for the treatment of relapsed refractory MM (RRMM).
Methods:
A systematic search of the literature was performed by searching PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, and Clinicaltrials.gov. Our search strategy included MeSH (Medical Subject Headings) terms and keywords for multiple myeloma, and isatuximmab including trade name and generic name from the date of inception to June 5, 2020. Initial databases search yielded 371 articles. After excluding review articles, duplicates, and non-relevant articles, we included five clinical trials reporting the efficacy and safety of ISA for RRMM.
Results:
Among a total of 526 enrolled patients, 517 patients were evaluated, ISA was given as a monotherapy in 84 patients and given as a part of the combination regimen in 433 patients. In these studies, patients were refractory to multiple lines of therapy.
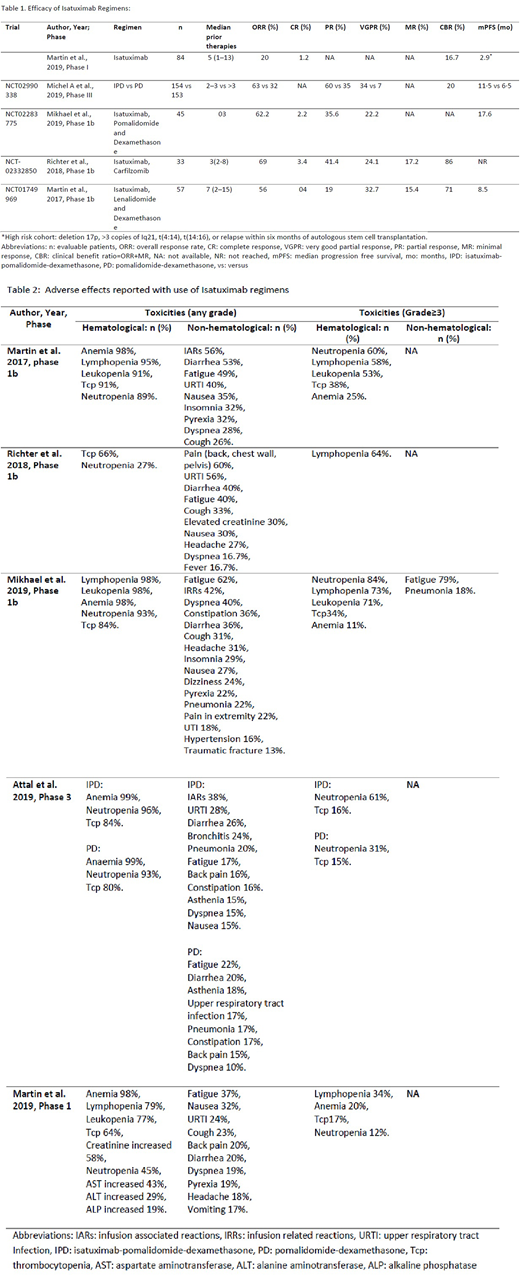
In phase III trial, Attal et al. (2019) studied ISA + Pomalidomide (P) and dexamethasone (d) (n=307) compared with Pd (n=153) with an overall response rate (ORR) of 63% (n=97) in ISA-PD group compared to 32% (n=49) in PD group. At a median follow-up of 11·6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 11·5 months (95% CI: 0·9-13·9) in the ISA-PD group versus 6·5 months (95% CI: 4·5-8·3) in the PD group; hazard ratio (HR) 0·596, (95% CI: 0·44-0·81; p=0·001).
Martin et al. (2019) studied ISA as monotherapy in RRMM patients with a median of five prior therapy and observed an ORR of 20 % (n=17) and clinical benefit rate (CBR) of 16.7 % (n=14). For the high-risk cohort, the ORR was 16.7% (3/18), and CBR 27.8% and progression-free survival (PFS) was 2.9 months (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.87 to 5.49). In another phase 1b clinical trial by Mikhael et al. (2019) using ISA-Pd. It showed an ORR of 62.2% (n=28), and partial response (PR) of 35.6% (n=16) with median PFS of 17.6 months (95 % CI: 6.8-20.5 months). Richter et al. (2018) reported a phase 1b clinical trial of ISA in combination with carfilzomib with ORR of 69% (n=20), and PR of 41.4% (n=12). Martin et al. (2017) (phase 1b) studied ISA + lenalidomide + d. The ORR was 56% (n=29) and median PFS was 8.5 months (95 % CI: 4.73-16.59). The ORR of 31% was observed in the high-risk cohort. The majority of adverse effects were hematological: pancytopenia. The main non-hematological adverse effects encountered were infusion-related reactions, fatigue, upper and lower respiratory tract infections (table 02).
Conclusion:
Isatuximab showed promising responses for the treatment of RRMM, maximal responses were observed with combination regimens.
Anwer:Incyte, Seattle Genetics, Acetylon Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie Pharma, Astellas Pharma, Celegene, Millennium Pharmaceuticals.: Honoraria, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal